FRVT 1:1 Verification
Starting from July 2023, the FRVT has been rebranded and split into FRTE and FATE. This evaluation track is now available as FRTE 1:1 Verification. See our comments on our newest results there.
These comments provided by Neurotechnology are based on NIST FRVT 1:1 Verification evaluation results published on March 13, 2023.
Neurotechnology algorithm has been ranked in the top 3% of most accurate results for border control supervised (Visa Border, Border) and unsupervised (Kiosk) scenarios among 702 submissions by 255 providers. The submission was also among the top 3% of algorithms for accuracy with face masks from a total of 319 entries.
NIST has started the FRVT Ongoing evaluation of face verification algorithms in February 2017. Since then, 728 algorithms from 267 vendors were tested on 7 datasets of different complexity. Each vendor can submit multiple algorithms once every three months, but the report takes into account only 2 latest submissions per vendor. Thus, only 396 algorithms are analyzed in the current results table from NIST.
The chart below shows the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with highlighted line showing Neurotechnology algorithm.
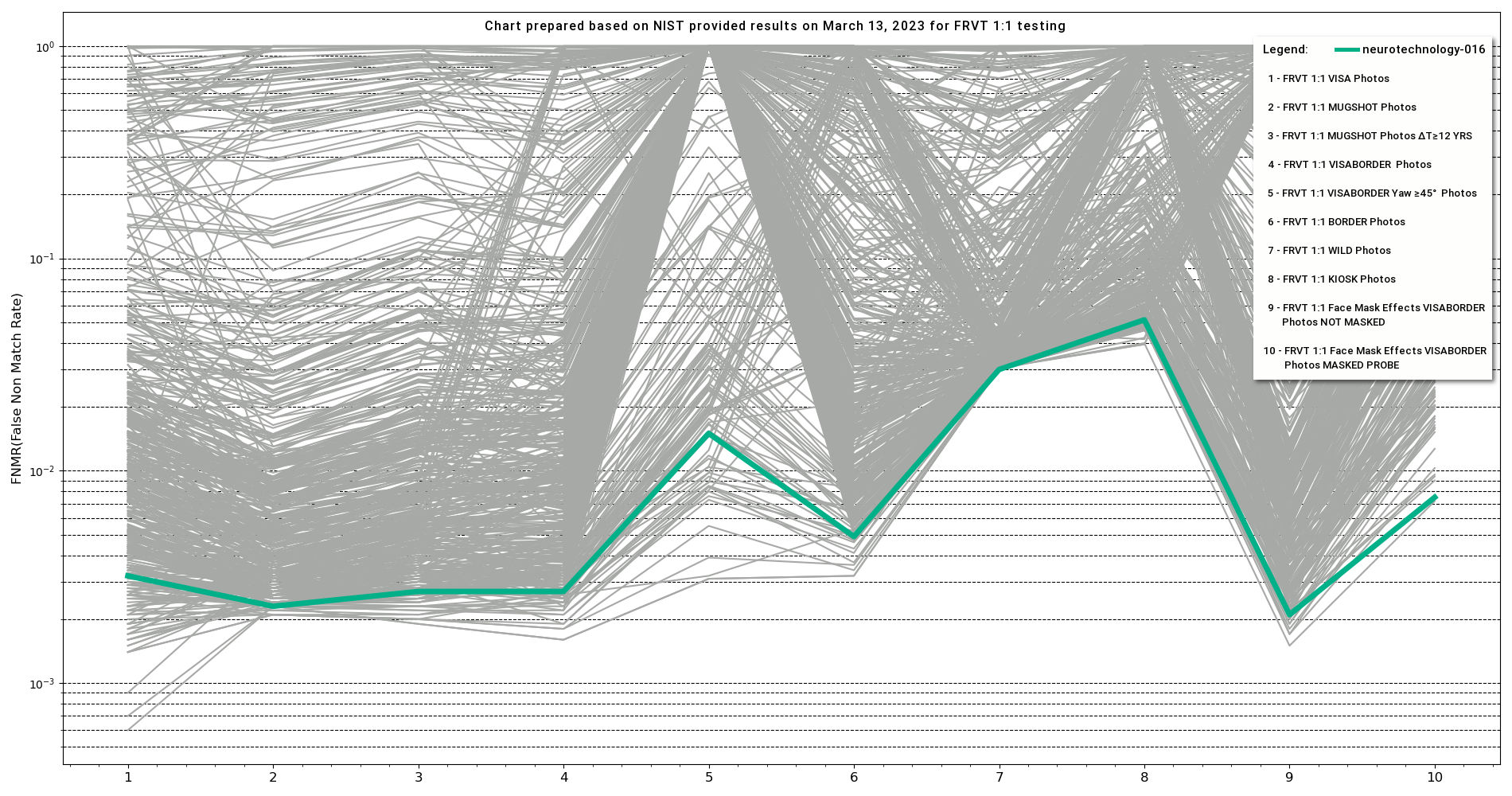
The horizontal axis on the chart corresponds to the performed tests, which are described below:
- FRVT 1:1 VISA Photos
- FRVT 1:1 MUGSHOT Photos
- FRVT 1:1 MUGSHOT Photos ΔT >12 YRS
- FRVT 1:1 VISABORDER Photos
- FRVT 1:1 VISABORDER Yaw ≥45° Photos
- FRVT 1:1 BORDER Photos
- FRVT 1:1 WILD Photos
- FRVT 1:1 KIOSK Photos
- FRVT Face Mask Effects VISABORDER Photos NOT MASKED
- FRVT Face Mask Effects VISABORDER Photos MASKED PROBE
Visa
The dataset represents typical photos of US visa applicants. According to the dataset description, the face images are generally high quality. Part of the images are live capture and the other part is photographed from paper photos.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.32% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.06% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- All face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- The comparisons were fully zero-effort, meaning there was no pre-grouping by gender, age or other covariates.
VISA dataset summary
- More than 100,000 unique persons.
- Part of the images are live capture and part are digitized paper photos.
- High quality images, with conformance with the ISO/IEC 19794-5 Full Frontal image type. Subjects' pose is generally excellent.
- Image size: 252x300 pixels.
- Interocular distance (IOD): 69 pixels.
- Subjects from more than 100 countries are represented, with significant imbalance due to visa issuance patterns.
- All ages are represented, including children, with imbalance due to visa issuance demand.
Mugshot
The dataset represents typical photos of suspects taken by law enforcement officers. The photos were taken in a controlled environment thus their quality is high.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.23% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.21% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- All face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
MUGSHOT dataset summary
- More than 1,000,000 unique persons.
- All images were live capture.
- High quality images, with conformance with the ISO/IEC 19794-5 Full Frontal image type. Subjects' pose is generally excellent.
- Variable image sizes.
- Interocular distance (IOD): from 34 to 297 pixels, with 113 pixels mean and 105 pixels median values.
- All subjects are from the United States.
- All subjects are adults.
Mugshots with 12+ years difference
The test was performed using the same dataset as in the MUGSHOT test above. The comparisons were performed only between mugshots representing same or different persons with age difference of 12 or more years between them.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.27% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.19% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- Age attribute was used to exclude template pairs, which represented same or different persons with age difference of less than 12 years at the capture moment, from the comparison.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Visa vs Border
The test was performed by comparing high-quality images from the VISA dataset against lower quality images from the BORDER dataset. Both datasets include subjects from more than 100 countries, with specific imbalances due to visa issuance patterns and border-crossing demographics correspondingly.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.27% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.16% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from Visa or Border datasets was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each pre-filtered template from the Visa dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the Border dataset
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Visa vs Border with 45+ degrees yaw angle difference
The test was performed using the same dataset as in the VISA BORDER test above. The comparisons were performed only between photos representing same or different persons with face yaw angle difference of 45 or more degrees between them.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 1.50% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.31% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from Visa or Border datasets was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Face yaw angle attribute was used to filter face template pairs for achieving the required yaw angle difference of 45 or more degrees.
- Each pre-filtered template from the Visa dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the Border dataset
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Border
The dataset is made of images obtained at border crossing. Images are taken by operators with webcams oriented towards cooperating subjects. The quality of the images may vary due to time-constrained capture and different illumination conditions.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.49% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.32% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- All pre-filtered face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Border dataset summary
- More than 1,000,000 unique persons.
- All images were live capture
- Variable image quality. There are role, pitch and yaw angle variations. There is some perspective distortion due to close range images. Background illumination is sometimes strong, so faces may be under-exposed. Some faces are partially cropped.
- Interocular distance (IOD): 38 pixels mean.
- Subjects from more than 100 countries are represented, with significant imbalance due to immigration patterns.
- All subjects are adults, with age distribution imbalance due to immigration patterns.
Wild
The dataset includes cropped photojournalism-style images of subjects, who do not make any efforts to be captured, thus their poses may vary very widely, and their faces can be occluded, including hair and hands. Image quality and resolution can also vary as the images are captured in random environment
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 3.00% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 2.93% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- All face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- The comparisons were fully zero-effort, meaning there was no pre-grouping by gender, age or other covariates.
WILD dataset summary
- More than 10,000 unique persons.
- All images were live capture.
- Variable image quality. There is wide yaw and pitch pose variation. Faces can be occluded, including hair and hands.
- Variable image sizes. Images were post-processed using a variable but generally tight crop of the head.
- All subjects are adults.
Kiosk
The dataset is made from images. which were captured from cooperating subjects in a partially controlled environment. Images' quality varied due to an automated, non-supervised capture method.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 5.19% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 3.94% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- All face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- The comparisons were fully zero-effort, meaning there was no pre-grouping by gender, age or other covariates.
KIOSK dataset summary
- All images were live capture.
- Many images have a considerable downward pitch angle.
- In some images, faces are partially cropped.
- Some images have other faces in the background.
Visa vs Border, Not masked and Masked Probes
These tests are part of separate FRVT Face Mask Effects evaluation, which used VISA and BORDER datasets from the FRVT 1:1 evaluation.
VISA BORDER NOT MASKED scenario
- The testing scenario is the same as the VISA BORDER from the FRVT 1:1, except that the resulting FNMR value is obtained using a different FMR value.
- Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.21% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR.
- The most accurate contender showed 0.15% FNMR at the same FMR.
VISA BORDER MASKED PROBE scenario
- One original image from the VISA dataset was used to create one face template.
- Each original image from the BORDER dataset was post-processed in five different ways to create synthetic lower face part occlusions as if the subjects wear face masks (see the figure below). One face template was created from each variant of the modified image.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each pre-filtered template from the VISA dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the BORDER dataset with synthetic face masks.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.75% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR.
- The most accurate contender showed 0.72% FNMR at the same FMR.
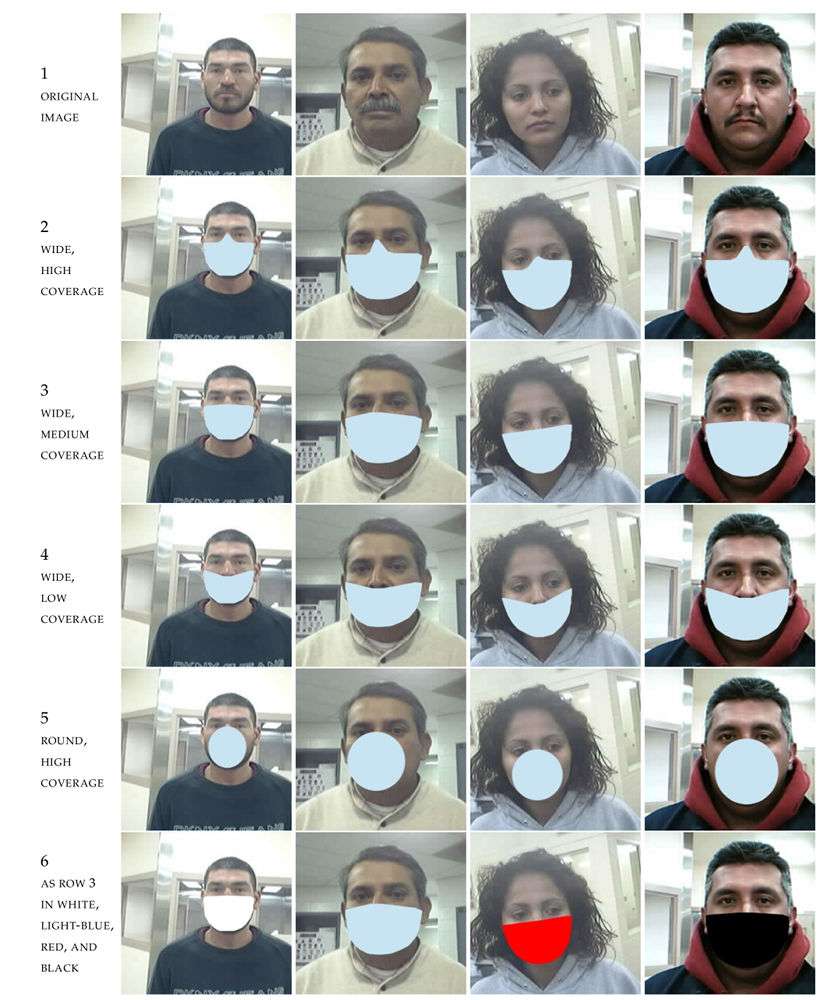

Image credit: B. Hayes, M. Ngan/NIST.